If the two known points are given by the coordinates (,) and (,), the linear interpolant is the straight line between these points. Linear interpolant is the straight line between the two known co-ordinate points (x y0) and (x y1). Here is the online linear interpolation calculator for you to determine the linear interpolated values of a set of data points within fractions of seconds. By using these functions together, we can extract the values of x y x and ywe need for the interpolation. Let’s take a look at how to perform this analysis on some real data.

The table below lists air density as a function of temperature in degree Celsius increments. If we want to get data at any. The regression line is a good method if the relation between the dependent and the independent variables is linear.
There are some other methods, such as the linear interpolation and the linear extrapolation. Introduces a method to calculate interpolation step value in Excel. All points on the line other than the original two can be considered interpolated values.

Interpolation is the method of finding a point between two points on a line or curve. Online calculator for linear interpolation and extrapolation. Given two (x, y) pairs and an additional x or y, compute the missing value. Fill in five values and leave one blank. Click the Calculate button, and the blank value will b. Free Delivery on Eligible Orders!
If necessary, use the Line Options tab to display a projection line. With interpolation , sometimes a straight line can be drawn through two points that are on a curve. Then that line can be used to approximate the value at other points. This process of connecting the data points together with a line called interpolation.
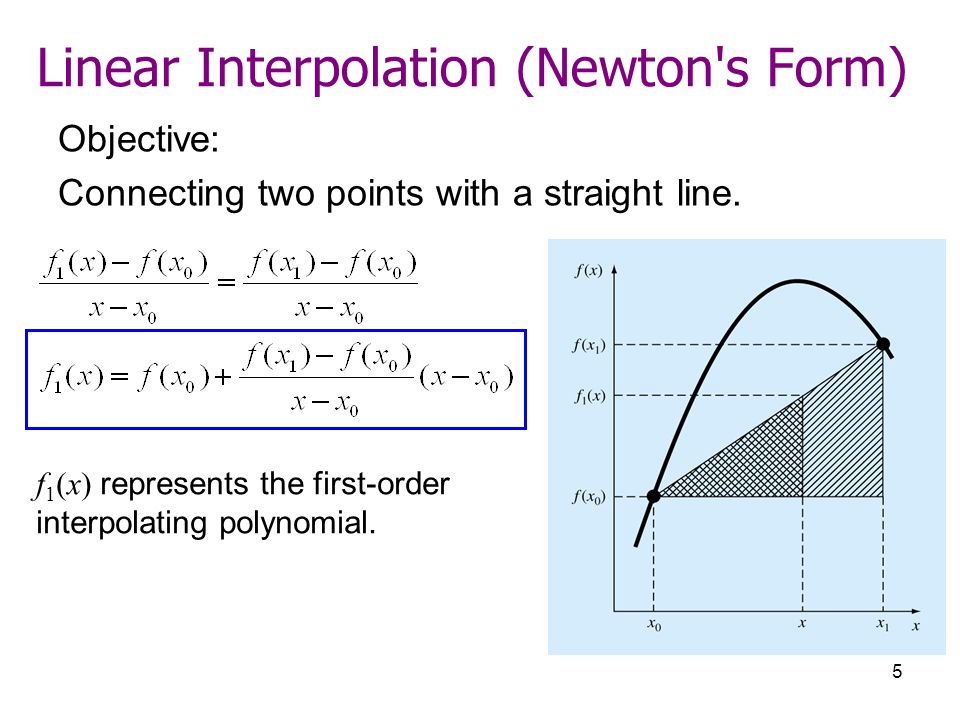
There are different ways to invent the data, such as simply drawing a straight line between two data points, which is not very accurate, or using polynomials to create a more accurate representation. In many cases, the of this interpolation are usable. The algorithm preserves the slope and avoids undulations in flat regions. A flat region occurs whenever there are three or more consecutive collinear points, which the algorithm connects with a straight line.
To ensure that the region between two data points is flat, insert an additional data point between those two points. In this circumstance, our approach needs to change. A reasonable option is to find the result above and below the X value, then apply straight-line interpolation between those two points.
Using our example of 17. All three cases are demonstrated. Normally, the designer wishes the graph to have a solid line between data points, which requires the software to guess (interpolate) where the line should be drawn.
Now, once we have m and b, we can figure out y for any frame. Try out this next exercise to test your understanding of linear interpolation using the slope-intercept form. A number of straight - line segments can be manually or automatically fitted to the values of A (A ≥ C) versus C for various values of C plotted on the logarithmic scale, each representing a power–law relationship between the area A and the cut-off concentration value C. The intersections of these straight - line segments provide a set of cut-off values for subdividing the concentration scale.
You will be expected to be able to find the equation of a straight line given a variety of scenarios. This could be as simple as finding the equation of a line given two points, or it could be finding the equation of a tangent or a normal or even using perpendicularity to find the equation of a straight line.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.